Illustrate the structure of water molecule
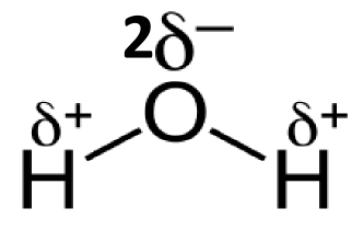
1 oxygen atom and 2 hydrogen atoms are joined together by ________ bond
1 oxygen atom and 2 hydrogen atoms are joined together by covalent bond
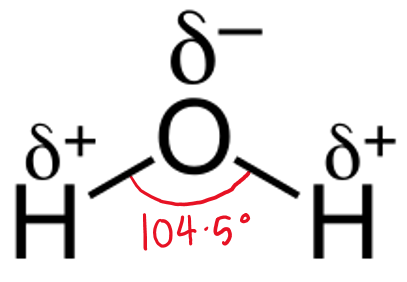
The 3 atoms (H2O) form a triangle with an angle of ____
1 water molecule can form maximum of 4 ________ _____ with 4 water molecules
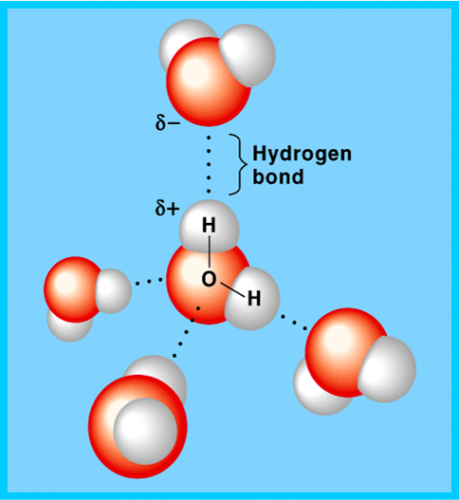
State 6 properties of water molecules
1. Polar molecules/Universal solvent
2. High specific heat capacity
3. High latent heat of vaporization
4. High surface tension
5. Maximum density at 4°C
6. Low viscosity
Carbohydrate is composed of ______, ________ & ______ atoms
Carbohydrate is composed of carbon, hydrogen & oxygen atoms
State 3 classes of carbohydrate with its example
Class - example
Monosaccharides - Glucose
Disaccharides - Maltose
Polysaccharides - Cellulose
Monosaccharide is the ________ ____ of sugar
Monosaccharides is the simplest form of sugar
Monosaccharide is the _______ for carbohydrates
Monosaccharides (1 sugar unit) is the monomer for carbohydrates
A disaccharide is
formed from 2 _______________
linked by __________ bond through
____________ process
A disaccharide is
formed from 2 monosaccharides
(two sugar units)
linked by glycosidic bond through
condensation process
Polysaccharides are polymer
formed from many _______________
linked by __________ ____
through ____________ process
Polysaccharides are polymer
formed from many monosaccharides
(many sugar units)
linked by glycosidic bond
through condensation process
Glucose (C6H12O6)
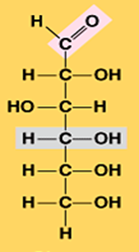
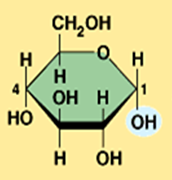
alpha glucose
beta glucose
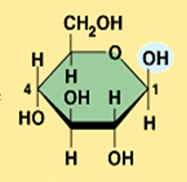
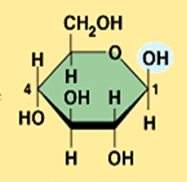
What is the structural difference between alpha glucose and beta glucose?
They differ in the orientation of the hydroxyl group ( –OH ) at carbon 1
What is condensation?
CONDENSATION
A chemical reaction in which 2 molecules are covalently bonded by removal of water molecule.
What is hydrolysis?
HYDROLYSIS
A chemical process in which a compound is broken down by addition of water.
Describe condensation
When a bond forms between 2 monomers, each monomer contributes part of water molecule that is released.
1 monomer provides an –OH group & the other provides a hydrogen.
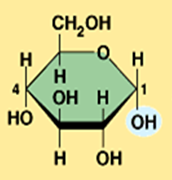
Illustrate alpha glucose (Monosaccharide)
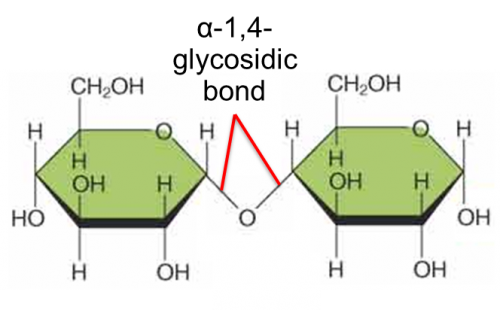
Illustrate maltose (Disaccharide)
Illustrate formation and breakdown of maltose
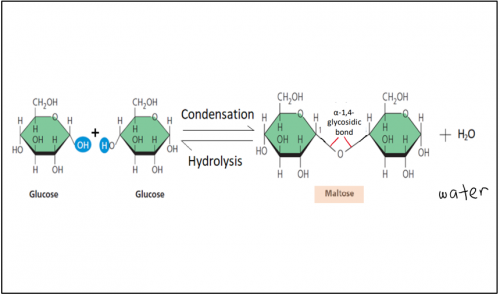
What is maltose?
Maltose is a disaccharide formed when two units of α-glucose joined with an
α-1,4- glycosidic bond.
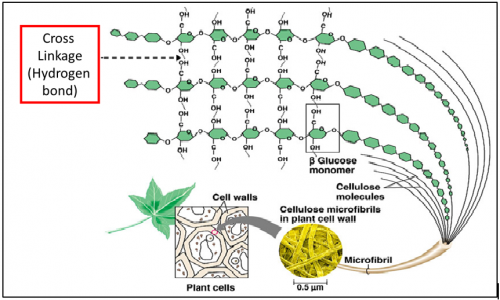
What is cellulose?
Cellulose is a polysaccharide made up of long chain of β-glucose joined with
β-1,4- glycosidic bond.
Illustrate beta glucose (Monosaccharide)
Cellulose (Polysaccharides)
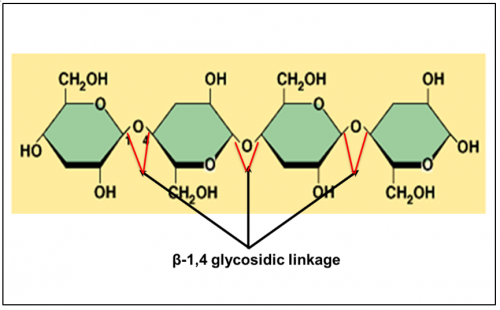
The ________ bond between the β-glucose chains gives cellulose its mechanical strength and chemical stability
Glycosidic bond is a type of ________ bond
Glycosidic bond is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
Lipid consists of
mainly ______ & ________ atoms;
and few ______ atom
Lipid consists of
mainly carbon & hydrogen atoms;
few oxygen atom.
Glycerol
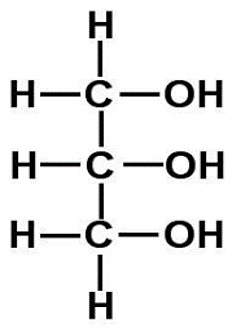
Describe glycerol
Glycerol is a
3 carbon compound with a hydroxyl (–OH) group attached to each carbon atom
Fatty acid
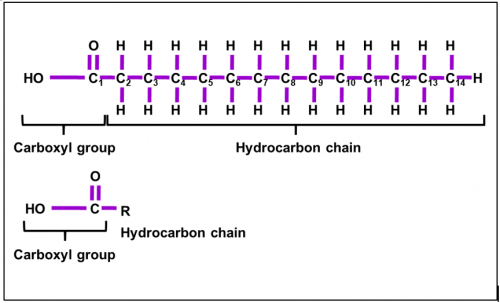
Describe fatty acid
Fatty acid is
a chemical compound consists of long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group
(–COOH) attached.
Fatty acid can be classified based on –
based on the presence of double bonds within hydrocarbon chain
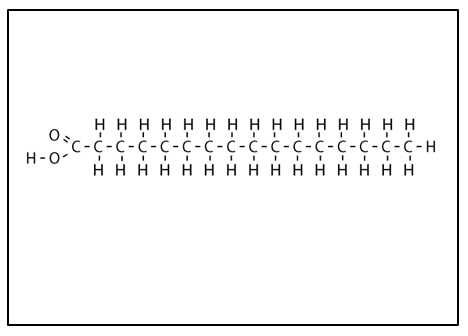
Saturated fatty acid
no double bond in the hydrocarbon chain
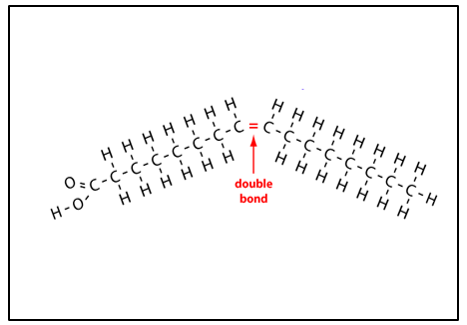
Unsaturated fatty acid
has double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain
Saturated fatty acid
Unsaturated fatty acid
State 3 major types of lipid with its example
Type - example
Triglyceride - fat and oils
Phospholipid - lecithin
Steroid - cholesterol
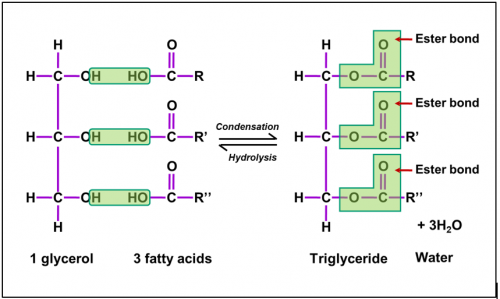
Triglyceride is made up from
Triglyceride is made up from
condensation of
1 glycerol molecule and
3 fatty acid molecules
Triglycerides
Phospholipid is made up from
Phospholipid is made up from
1 glycerol molecule,
2 fatty acid molecules
and 1 phosphate group
Phospholipid

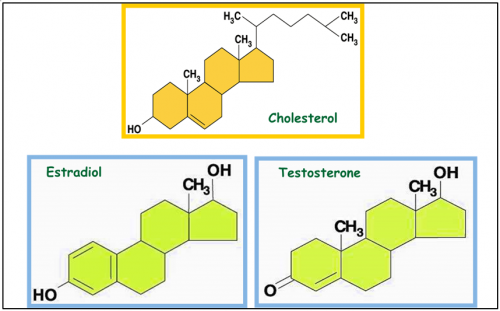
Steroid consists of
Steroid consists of
4 different rings
and different steroid will have different side chain
Steroid
What is monomer? What is polymer?
Monomer - 1 unit / a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
Polymer - Many repeating units
_____ _____ are the monomers that make up protein
Amino acids are the monomers that make up protein
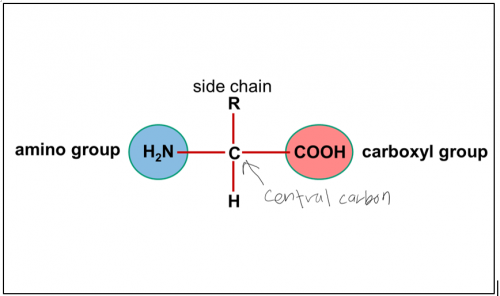
Describe amino acid
A chemical compound with a
carboxyl group,
amino group
and side chain (R group)
attached to the central carbon called alpha carbon.
Amino acid
Amino acids are __________ ; because it has both acidic & basic properties
Amino acids are amphoteric ; have both acidic (carboxyl group –COOH) & basic (amino group –NH2)
properties.
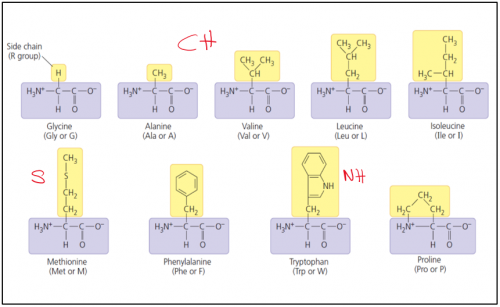
20 types of amino acid can be grouped into _ groups based on the characteristic of the side chain ( _ group)
20 types of amino acid can be grouped into 4 groups based on the characteristic of the side chain (R group)
State the 4 groups of amino acid:
i. Non polar / Hydrophobic
ii. Polar / Hydrophilic
iii. Acidic
iv. Basic
Non polar / hydrophobic amino acids
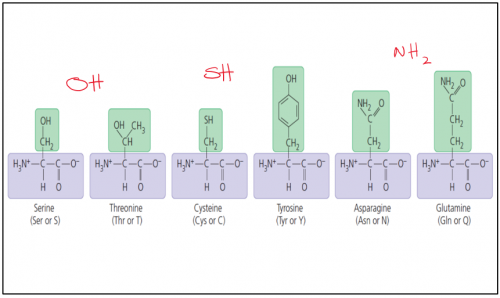
Polar / hydrophilic amino acids
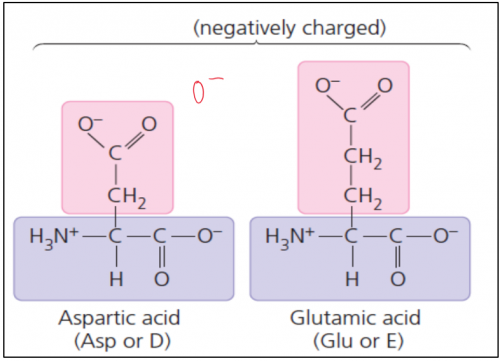
Acidic amino acids
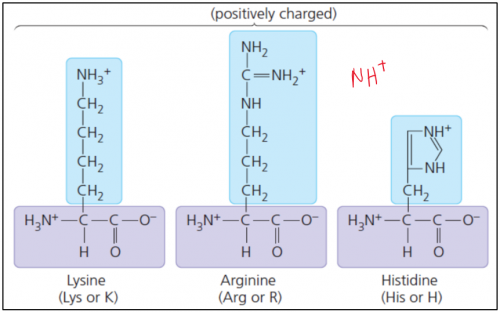
Basic amino acids
2 _____ _____ are joined together by ____________ process to form a dipeptide
2 amino acids are joined by condensation process to form a dipeptide.
What is dipeptide? What is polypeptide?
Dipeptide: 2 amino acid linked together.
Polypeptide: short chains of 2 or more amino acids.
Illustrate formation and breakdown of dipeptide
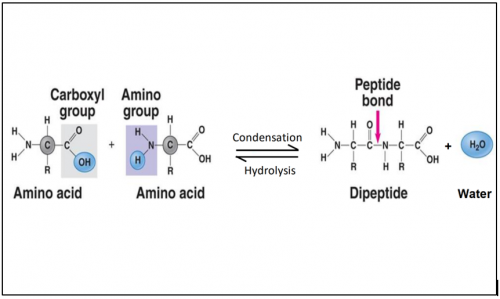
Describe condensation process in the formation of dipeptide
The carboxyl group of one amino acid is linked to the amino group of the incoming amino acid.
In the process, a molecule of water is released.
Amino acids are joined by _______ bond.
Amino acids are joined by peptide bond.




