Three types of ground tissues :
Parenchyma
Collenchyma
Sclerenchyma
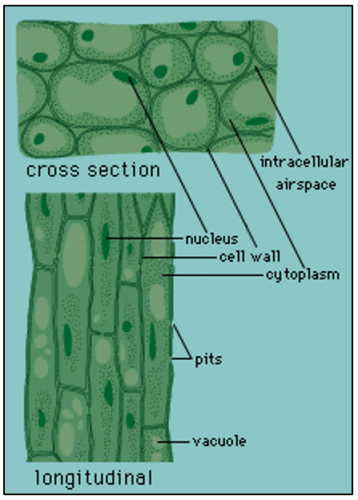
• Living cells with nucleus at maturity
• Primary cell walls are thin and flexible
(consists of cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin)
• Cells are loosely packed with intercellular air spaces
Parenchyma's structure
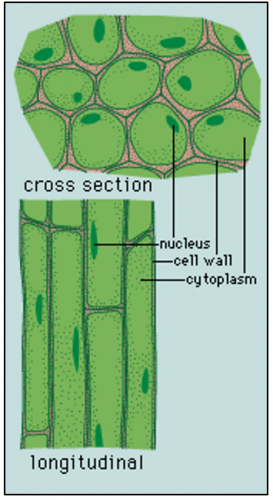
• Living cells with nucleus at maturity
• Primary cell walls are unevenly thickened at corners
(consists of cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin)
• Cells are closely packed, no intercellular air spaces
Collenchyma's structure
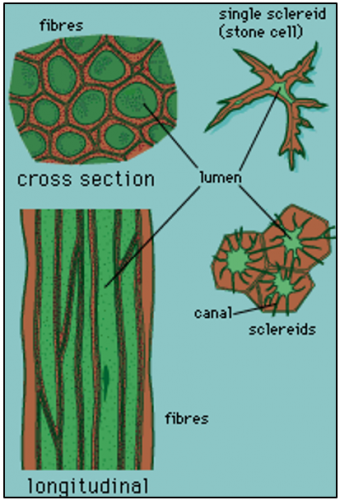
• Dead cells without nucleus at maturity
• Secondary cell walls are evenly thickened and lignified
(consists of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin)
• Cells are tightly packed together, no intercellular space
Sclerenchyma's structure
Parenchyma
Collenchyma
Sclerenchyma
Function of Parenchyma
Store organic substances -> from large central vacuole
Photosynthesis -> the mesophyll cells contain chloroplast
Gaseous exchange -> due to large intercellular space
Attract pollinator -> as some cells contain chromoplast
Function of Collenchyma
Support in herbaceous plant or young parts of plant
Gives mechanical strength and flexibility – to allow the cell to expands as it grow
Function of Sclerenchyma
Support and protection from mechanical damage
Provide mechanical strength and rigidity to the plant
Which type of ground tissue mostly found in leaf, stem and root?
Parenchyma
Which type of ground tissue mostly found young parts of the plant shoot and petioles?
Collenchyma
Sclereid is a type of ___________ that is found in stones of cherry
Sclereid is a type of sclerenchyma that can be found in stones of cherry
Fibre is a type of ____________ that can be found in wood or inner bark.
Fibre is a type of sclerenchyma that can be found in wood or inner bark.




