Carbohydrate is composed of ______, ________ & ______ atoms
Carbohydrate is composed of carbon, hydrogen & oxygen atoms
State 3 classes of carbohydrate with its example
Class - example
Monosaccharides -
Glucose, Galactose, Fructose
Disaccharides -
Maltose, Lactose, Sucrose
Polysaccharides -
Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose
Monosaccharide is the ________ ____ of sugar
Monosaccharides is the simplest form of sugar
Monosaccharide is the _______ for carbohydrates
Monosaccharides (1 sugar unit) is the monomer for carbohydrates
A disaccharide is
formed from 2 _______________
linked by __________ bond through
____________ process
A disaccharide is
formed from 2 monosaccharides
(two sugar units)
linked by glycosidic bond through
condensation process
Polysaccharides are polymer
formed from many _______________
linked by __________ ____
through ____________ process
Polysaccharides are polymer
formed from many monosaccharides
(many sugar units)
linked by glycosidic bond
through condensation process
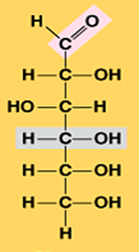
Glucose (C6H12O6)
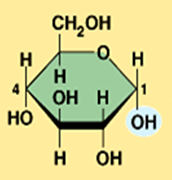
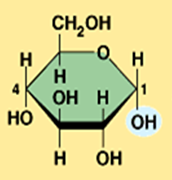
alpha glucose
beta glucose
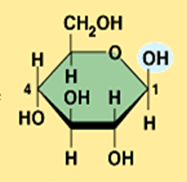
What is the structural difference between alpha glucose and beta glucose?
They differ in the orientation of the hydroxyl group ( –OH ) at carbon 1
What is condensation?
CONDENSATION
A chemical reaction in which 2 molecules are covalently bonded by removal of water molecule. to form polymer
What is hydrolysis?
HYDROLYSIS
A chemical process in which a compound is broken down by addition of water. to form monomer
Describe condensation
When a bond forms between monomers, each monomer contributes part of water molecule that is released.
Illustrate alpha glucose (Monosaccharide)
Illustrate maltose (Disaccharide)
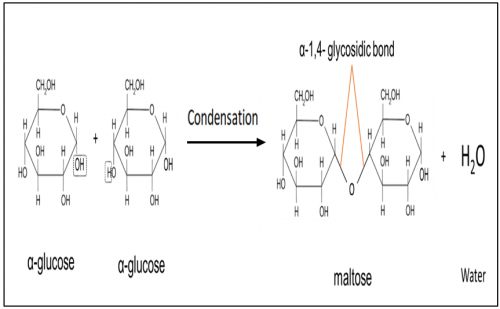
Illustrate formation of maltose
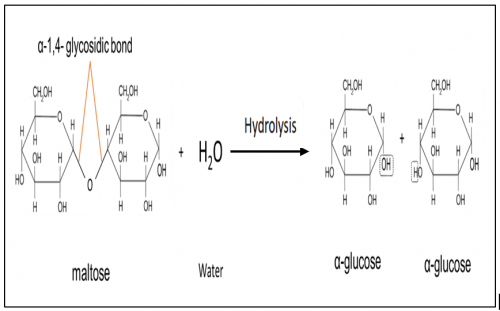
Illustrate breakdown of maltose
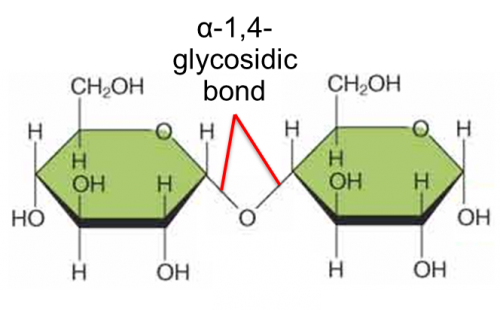
What is maltose?
Maltose is a disaccharide formed when two units of α-glucose joined with an
α-1,4- glycosidic bond.
What is cellulose?
Cellulose is a polysaccharide (polymer) made up of long chain of β-glucose (monomer) joined with
β-1,4- glycosidic bond.
Illustrate beta glucose (Monosaccharide)
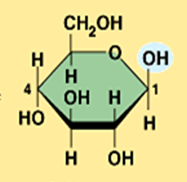
Starch is a ______________ formed from monomer _____ glucose
Starch is a polysaccharide (polymer) formed from monomer alpha glucose
Cellulose (Polysaccharides)
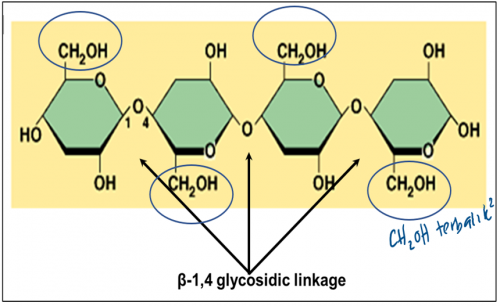
The ________ bond between the β-glucose chains gives cellulose its mechanical strength and chemical stability
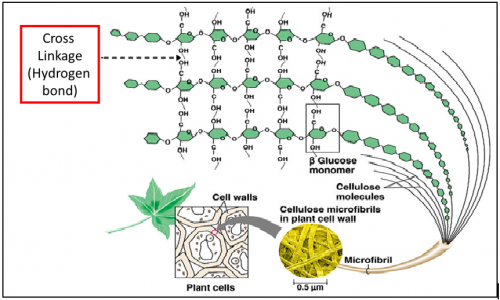
What is the function of cellulose?
Major component of cell walls which provide structural support to plant cell
Starch is made up of _______ (unbranched chain) and ___________ (branched chain)
Starch is made up of amylose (unbranched chain) and amylopectin (branched chain)
Amylose is an unbranched chain because it does not have _ __ _________ bond
Amylose is an unbranched chain because it does not have α-1,6- glycosidic bond.
Amylopectin is a branched chain because it does have _ __ _________ bond
Amylopectin is a branched chain because it does have α-1,6- glycosidic bond.
What is amylose?
Amylose is a polysaccharide (polymer) made up of long chain of α-glucose (monomer) joined with
α-1,4- glycosidic bond.
Amylose in Starch (Polysaccharides)
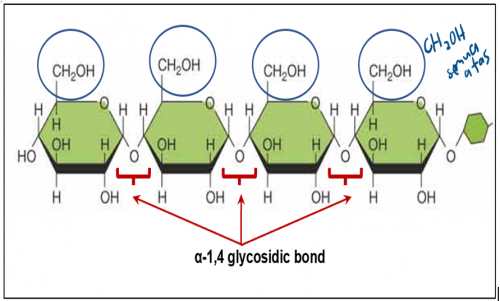
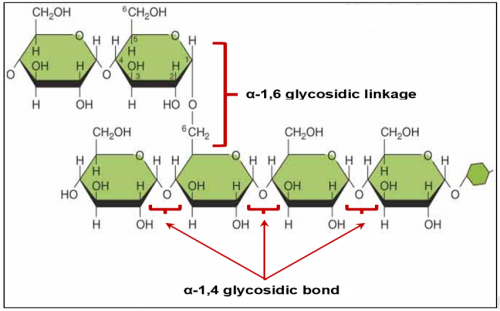
What is amylopectin?
Amylopectin is a polysaccharide (polymer) made up of long chain of α-glucose (monomer) joined with
α-1,4- glycosidic bond and α-1,6- glycosidic bond.
What is glycogen
Glycogen is a polysaccharide (polymer) made up of long chain of α-glucose (monomer) joined with
α-1,4- glycosidic bond and α-1,6- glycosidic bond.
How is glycogen similar to amylopectin?
- Both have alpha glucose as monomer
- Both have its monomers linked together by α-1,4 glycosidic bond and α-1,6 glycosidic bond
- Both structure are formed by condensation
How is glycogen different from amylopectin?
Glycogen is
-highly branched
-more water soluble
-energy storage in animal cell
If in plant cell - its amylopectin
If in animal cell - its glycogen
What is the function of starch (in plant) and glycogen (in animal)?
Energy storage because the are compact and easily hydrolyzed
Glycosidic bond is a type of ________ bond that joins a ____________ (sugar) molecule to another, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
Glycosidic bond is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.




