Examples of structured problems are:
– Network flow
– Shortest path – Spanning tree
Examples of Network Flow
• Assignment
• Transportation
• Transshipment
• Maximum flow
General Network Flow Problem
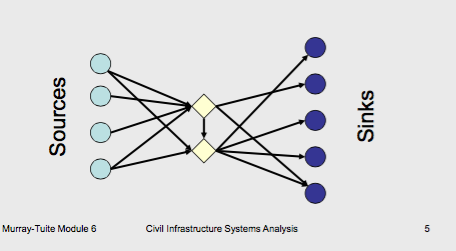
minimum cost network flow problem
– Each source (job) can supply one unit
– Each sink (machine) demands one unit
– Each arc has a capacity of one unit of flow and a cost taken from the table
Maximum Flow Problem
• Variation on the general minimum cost network flow problem
• Find the maximum flow that can be sent between a single source and a single sink
– Each arc has a capacity which limits the amount of flow
– No cost is associated with using the arc
Min-cut max-flow theorem:
the maximum flow possible is equal to the capacity of the minimum cut disconnecting the source and the sink
Spanning Tree
• A spanning tree of the network G(N,A) is any tree of the network G which contains the entire set of nodes N
• We would like to decrease the number of city pairs connected by direct non-stop flights
link painting
• Exploring the link inclusion is often called link painting
–Every link that will be part of the spanning tree should be painted green
–The links that will not be part of the spanning tree should be painted red
Spanning Tree
• When considering a particular link
we are exploring whether that link would create a cycle
Spanning Tree
• During creation of the tree
some links are already included in the tree, while others are outside the tree
– Links included in the tree create one or more connected components
minimal spanning tree
• Every link in the network is characterized by the appropriate length
• The length of a spanning tree represents the sum of the link lengths that form the tree
• Different spanning trees usually have different lengths
• The minimal spanning tree has the least length for a given transportation network
To solve spanning tree problem
1. List the links in user defined order
2. Add links in that order until all nodes reached
(objective=minimum number of nodes)
To solve minimum spanning tree
1. List the links in descending order
2. Add links in that order until all nodes reached
(objective=minimize distance)
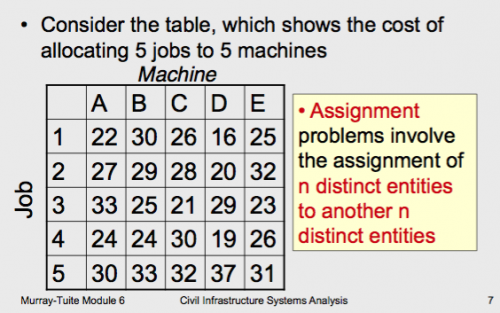
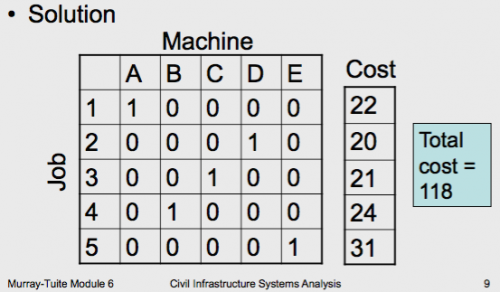
Assignment Problem can be viewed as a minimum cost network flow problem
– Each source (job) can supply one unit
– Each sink (machine) demands one unit
– Each arc has a capacity of one unit of flow and a cost taken from the table
Costs in transportation problem with variable and fixed.
These costs are obtained by adding the variable production costs to the transportation costs
Suppose we take the transportation problem we just considered and add the additional information that a new depot has become available where:
– The depot has a cost per ton of throughput of $0.70
– The cost of shipping from factories A, B, and C to the depot is 0.1, 0.3, and 0.7 ($/ton), respectively
– The cost of shipping from the depot to customers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 is 0.7, 0.9, 1.1, 0.8, 0.6, and 0.9 ($/ton), respectively
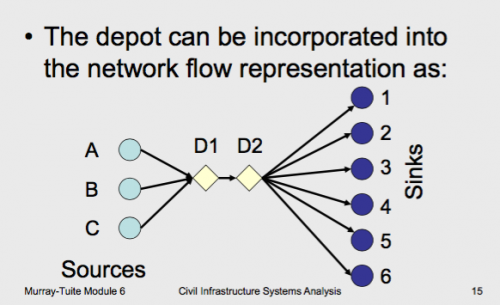
Frequently in transportation problems
Frequently, goods are not transported directly from factories to customers but are shipped (transshipped) via intermediate locations




