activation energy
the least amount of energy required to activate atoms or molecules to a state in which they can undergo a chemical reaction.

adaptation
any alteration in the structure or function of an organism or any of its parts that results from natural selection and by which the organism becomes better fitted to survive and multiply in its environment.

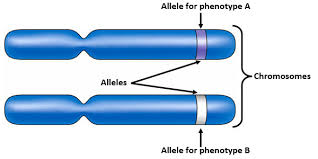
allele
any of several forms of a gene, usually arising through mutation, that are responsible for hereditary variation.
abiotic
of or characterized by the absence of life or living organisms.
accuracy
the condition or quality of being true, correct, or exact; freedom from error or defect; precision or exactness; correctness.
amino acids
any of a class of organic compounds that contains at least one amino group, –NH 2 , and one carboxyl group, –COOH: the alpha-amino acids, RCH(NH 2)COOH, are the building blocks from which proteins are constructed.
amphibian
any cold-blooded vertebrate of the class Amphibia, comprising frogs and toads, newts and salamanders, and caecilians, the larvae being typically aquatic, breathing by gills, and the adults being typically semiterrestrial, breathing by lungs and through the moist, glandular skin.

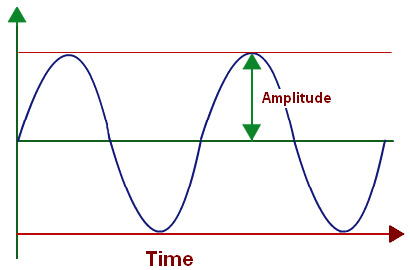
amplitude
the state or quality of being ample, especially as to breadth or width; largeness; greatness of extent.
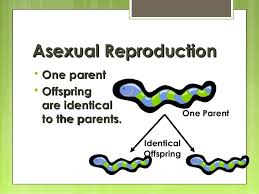
asexual reproduction
reproduction, as budding, fission, or spore formation, not involving the union of gametes.
atmosphere
the gaseous envelope surrounding the earth; the air

atom
the smallest component of an element having the chemical properties of the element, consisting of a nucleus containing combinations of neutrons and protons and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus by electrical attraction
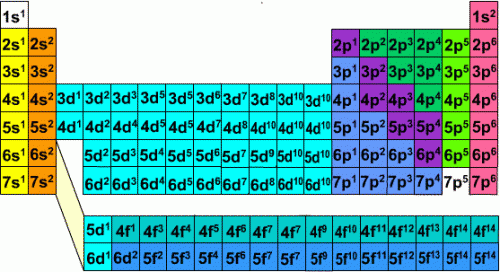
atomic configuration
the relative disposition or arrangement of the parts or elements of an atom
atomic theory
Physics, Chemistry. any of several theories describing the structure, behavior, and other properties of the atom and its component parts.
attract
to draw by a physical force causing or tending to cause to approach, adhere, or unite; pull
axis
a central or principal structure, about which something turns or is arranged
balance
a state of equilibrium or equipoise; equal distribution of weight, amount
base
the bottom support of anything; that on which a thing stands or rests
Big Bang Theory
a theory that deduces a cataclysmic birth of the universe (big bang)from the observed expansion of the universe, cosmic background radiation, abundance of the elements, and the laws of physics
biodiversity
diversity among and within plant and animal species in an environment
biotic
pertaining to life
bird
an animal having a body covered with feathers, forelimbs modified into wings, scaly legs, a beak, and no teeth, and bearing young in a hard-shelled egg
calorie
an amount of heat exactly equal to 4.1840 joules





