magnetism (magnetic)
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to amagnetic field, which acts on other currents and magneticmoments. Every material is influenced to some extent by amagnetic field.
mammal
any vertebrate of the class Mammalia, having the body more or less covered with hair, nourishing the young with milk from the mammary glands, and, with the exception of the egg-laying monotremes, giving birth to live young.

mantle
something that covers, envelops, or conceals:
mass
a body of coherent matter, usually of indefinite shape and often of considerable size:
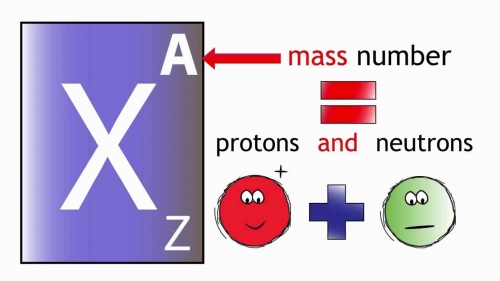
mass number
the integer nearest in value to the atomic weight of an atom and equal to the number of nucleons in the nucleus of the atom.
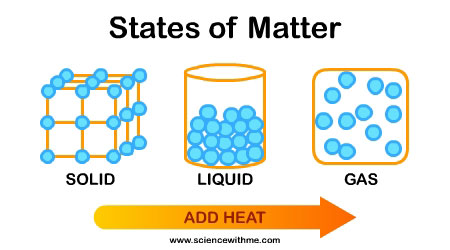
matter
the substance or substances of which any physical object consists or is composed:
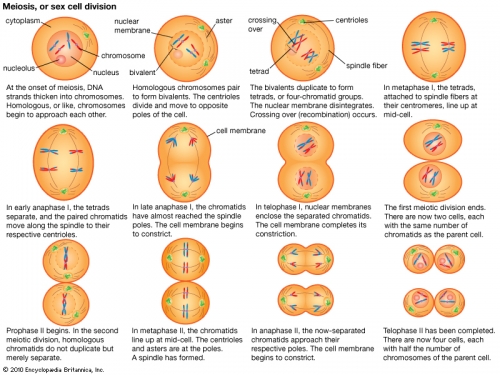
meiosis
part of the process of gamete formation, consisting of chromosome conjugation and two cell divisions, in the course of which the diploid chromosome number becomes reduced to the haploid.
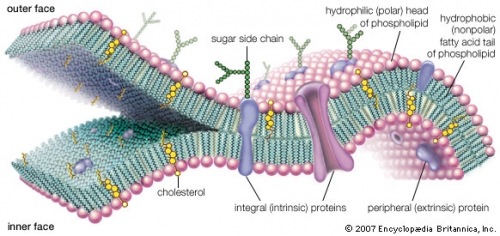
membrane
Anatomy. a thin, pliable sheet or layer of animal or vegetable tissue, serving to line an organ, connect parts, etc.
metamorphic rock
Rock that was once one form of rock but has changed to another under the influence of heat, pressure, or some other agent without passing through aliquid phase.

meteor
a meteoroid that has entered the earth's atmosphere.

microscopic
very small; tiny.

mitosis
the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell.